Papillomas are benign neoplasms located on the skin and mucous membranes. They arise from the activation of the human papillomavirus (HPV) and are of many different types. Some of them are harmless and create only a cosmetic defect, others are potentially dangerous and can develop into a cancerous tumor.
The mechanism of origin of papillomas
The appearance of a certain type of tumor depends on the type of virus with which a person is infected. Distinguish between low oncogenic strains in which the growths do not pose a great danger to the carrier, and highly oncogenic. Tumors appear due to the papillomavirus, whose action leads to excessive cell division, as a result of which growth gradually increases.
"Safe" papillomas usually appear on the skin, while the most disturbing are localized in the mucous membranes.Such neoplasms usually cause highly oncogenic types of the virus. For women, the appearance of growths in the genital area can be dangerous for cervical cancer.
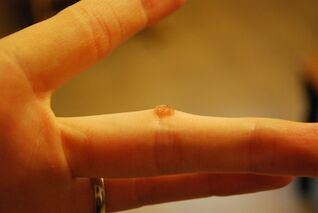
Common papillomas (warts)
One of the most common manifestations of HPV, known as "warts". Their appearance is usually due to the action of low oncogenic strains transmitted through contact and daily.
Warts usually appear on the fingers, palms, soles or feet.
Externally, they resemble small papillary neoplasms with homogeneous structures. Ordinary papillomas are soft to the touch, at the beginning of the disease their pigmentation is weak: the color is practically indistinguishable from body color.
However, as the disease progresses, the growth grows and begins to darken. Sometimes hair can grow in the center of the wart.
Filiform papillomas
This type of papilloma got its name because of the small legs, thanks to which the neoplasm stands out above the surface of the skin. The growth has an elongated shape and has a size of about 5 mm. Most often papillomas are localized in places where the skin is thinnest:
- breasts;
- neck;
- eyelids;
- groin area; armpits.
Filamentous papillomas are more common in patients over the age of 45, but sometimes occur in young people. Growth usually increases as the disease progresses.Gradually, they begin to stretch more.
The head of the papillomas is yellow or pink, there is no pronounced pigmentation. Keratinized neoplasm is rare. No pain is observed in trauma. Several others may appear at the site of the damaged filamentous papilloma. If the growths are located on the face, it is advisable to stop using scrubs or brushes. In the armpits, papillomas are also often injured by razors, which can adversely affect the patient's health.
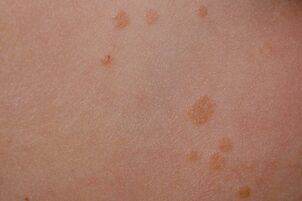
Flat papillomas
This form of papilloma is also localized on the skin and resembles small plaques. Flat papillomas have a yellowish tinge, the size does not exceed 1-2 mm. The structures are dense in structure, their root is under the skin. Therefore, pain may occur during injury or pressure. Also, this structural feature sometimes leaves scars after removal of the accumulation.
Typical symptoms accompanying flat papillomas:
- redness of the skin around the growth;
- itching;
- pain on touch;
- inflammation.
Usually growths appear on the face or hands, but sometimes they also appear on the genitals. In women, they are usually located on the labia majora, in men, on the scrotum or anus. Flat papillomas rapidly increase in size and bleed when traumatized.
Genital warts
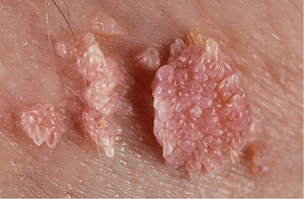
These growths are usually found in the groin or mucous membranes. They are caused only by strains of HPV that appear during unprotected sex. Most often they hit:
- vagina;
- vulva;
- cervix;
- anus area;
- scrotum;
- penis.
The growths are similar to thin papillae, they are small - 2-3 mm. The virus is not usually limited to the appearance of a single neoplasm. Warts are characterized by the appearance of several growths at once, gradually merging with each other. Neoplasms grow rapidly and grow. At this time, their shape begins to resemble cauliflower inflorescences.
Genital warts are considered one of the most dangerous types of papillomas.In addition to the fact that these growths are able to degenerate into a malignant tumor, they are often accompanied by infection. Also, neoplasms are prone to recurrence after removal, so patients will need to undergo regular checkups to monitor HPV levels.
In rare cases, warts can form on internal organs such as the walls of the stomach or rectum. In this case, it is impossible to independently diagnose the presence of a tumor. The lack of specific symptoms can become a problem in the diagnosis and treatment of the disease.
Lewandowski-Lutz papillomas
Quite a rare type of papilloma. They most often appear in the legs and arms. A distinctive feature of the growths are the uneven edges. They are usually brown in color, but can sometimes have a dark red tinge. This form of the disease can also contribute to the transformation of neoplasms into malignant, so patients should consult a doctor as soon as possible.
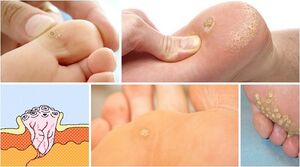
Plantar warts
These growths are more common in children and adolescents, rarely occurring in adulthood. It is considered a common reaction of the body to reduced immunity, accompanied by trauma to the sole due to uncomfortable shoes. Unlike ordinary calluses, the wart is rough and has jagged edges. Also, the skin pattern is clearly visible on the callus.
Plantar warts are characterized by a small spot on the surface of the skin and a large base that grows subcutaneously. He is usually completely keratinized due to constant abrasion when walking. Over time, the growth increases, pressing or touching them provokes discomfort and pain.Due to the nature of the structure, it is difficult to remove the wart from the skin, as most of it is inside. Therefore, after removal it is often necessary to put stitches and a scar may remain at the site of the procedure.
Juvenile papillomas
Most infections occur in young children under the age of 5, as the infection usually occurs at birth. If a pregnant woman is a carrier of the papilloma virus and has genital warts in the vaginal area, the baby is more likely to become infected.
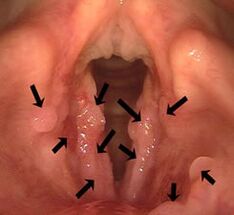
Juvenile papillomas located on the skin are not dangerous. However, they can also be located in the larynx, which can lead to difficulty breathing for the baby. In the initial stage there are no signs of the disease. After a while, the following symptoms appear:
- feeling of a lump in the throat;
- difficulty swallowing saliva or food;
- impaired respiratory function.
Older children may experience voice changes, which are a sign of a damaged relationship. Papillomas can grow and provoke asthma attacks, which can one day lead to complete cessation of breathing.
Papillomatosis
Papillomatosis is a condition in which the number of neoplasms increases dramatically and spreads throughout the body. It is also called generalized papilloma virus. Usually a large accumulation of papillomas occurs on the hands, face, in the genital area. Papillomatosis, which occurs in the mucous membranes or internal organs, is potentially dangerous to humans.
Papillomatosis is most often mentioned when young papillomas appear in the area of the larynx. They are the ones who tend to outgrow it.
Conclusion
Despite the fact that there are relatively safe forms of papillomas, each of them needs regular examination by a specialist. This will help keep their growth under control and remove it immediately if necessary. It is also important to remember that the presence of neoplasms is an indicator of papillomavirus infection, which also requires timely therapy.























